From TKWB - Traditional Knowledge World Bank
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| GENERAL DEFINITION OF THE TECHNIQUE |
|
| Technique: |
TORRENT STREETS |
|
Definition characters description and diffusion
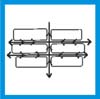
In areas where there are long periods of drought followed by short periods of heavy rainfall and flooding, torrent streets are used as a way to collect and guide the rain water so that it can be used and stored efficiently.
General characters description and diffusion
The main water resource of the sinuous M'zab valley, the Algerian Sahara desert, comes from the flooding that occurs every three of twn years and the whole valley is organized on the basis of this event. Large water intakes intercept the flow and distribute it to the tilled fields. The narrow streets enclosed between the high walls, which surround the gardens, become torrents that convey the precious water. Apertures are made in the walls to draw in the quantity of water needed for each garden where a further series of little channels, bridges and basins ensure the irrigation of fruit and vegetable gardens. This water distribution technique of the torrent-streets is still working in the Wadi Dhahr at 15 km from the town of San'a in Yemen where during the rainfalls the small walled streets convey the water to the gardens that are arranged on a slightly lower level by means of sluice gates situated in the enclosures. The whole system works by gravity and determines a rigorous organization which fully functions only when the sporadic floods occur and the pathways turn into watercourses.
Advantages and sustainability
Torrent streets guide and collect rainwater from heavy rainfalls so that it can be stored and used for irrigation in times of no rain fall.
Images
Deepening
|
TRADITIONAL TECHNIQUE DATA
| Author: |
|
| Other authors: |
|
| Reference: |
|
|
|